7.6. Add layers
Raster and vector geodata are uploaded to Web GIS by creating Raster layer and Vector layer resources respectively.
Note
The size limit for uploaded files depends on the selected plan. For Premium - 2 GiB, for Free - 128 MiB and Mini - 256 MiB.
See other data requirements for raster and vector layers below.
7.6.1. Vector layer from file
In NextGIS Web you can create vector layers based on variours formats, use PostGIS connection or create an empty vector layer that has attribute structure but no features.
7.6.1.1. Input data requirements
Source files could be in the following formats:
Point layers can also be created from CSV and XLSX files, the coordinates should be in the ‘lat’ and ‘lon’ columns. Watch the process of creating such a layer in the video:
Watch on youtube.
Use NextGIS Connect if you need to upload data in other formats.
Note
In case of ESRI Shapefile, all components (dbf, shp, shx, prj and other files) should be compressed to a zip-archive.
File size limits depend on your subscription plan.
Warning
Avoid using Unicode symbols in data field names. While such data can be uploaded to the Web GIS and displayed on Web Maps, you can experience problems working with it in NextGIS Mobile or visualization (especially if labels are using such fields). Use plain Latin for field names and set up field aliases to show Unicode names.
If input data layer contains fields named id (ID) or geom (GEOM), they will be renamed on import. If id has meaningful identifiers, they will automatically be turned into internal FIDs.
7.6.1.2. Creation process
Navigate to the resource group (folder) in which to create a vector layer. Press Create resource button and select Vector layer (see Pic. 7.45.).
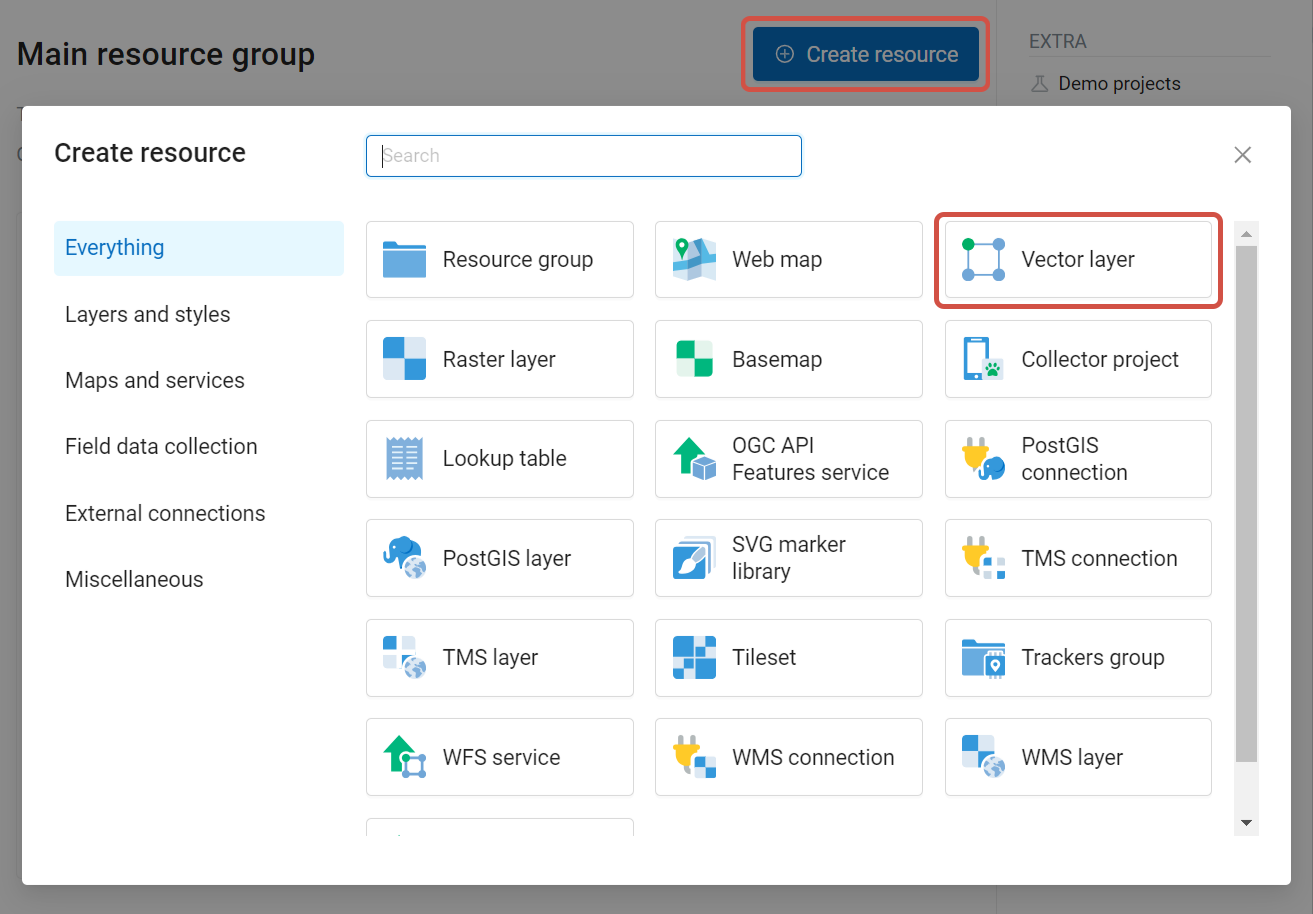
Pic. 7.45. Selection of “Vector layer” resource type
In the opened tab you need to upload a geodata file in ESRI Shapefile (zip-archive), GeoJSON, KML, GML or GeoPackage format. For CSV and XLSX only points are supported, coordinates must be put in lat and lot columns.
The upload dialog indicates the maximum file size allowed on your subscription plan (Pic. 7.46.). Web GIS can process multi-layer datasets. If an archive contains several layers, then after it is uploaded, you will be asked to select which layer will be used for creating Vector layer resource.
Below it is proposed to define advanced options for creating a vector layer. Depending on the quality of the data you can define how to handle geometry errors when uploading a file, select the type of geometry, the presence/absence of multigeometries, Z-coordinates and the source of the FID (FID field, determine automatically or indicate from a particular field). More about advanced options.
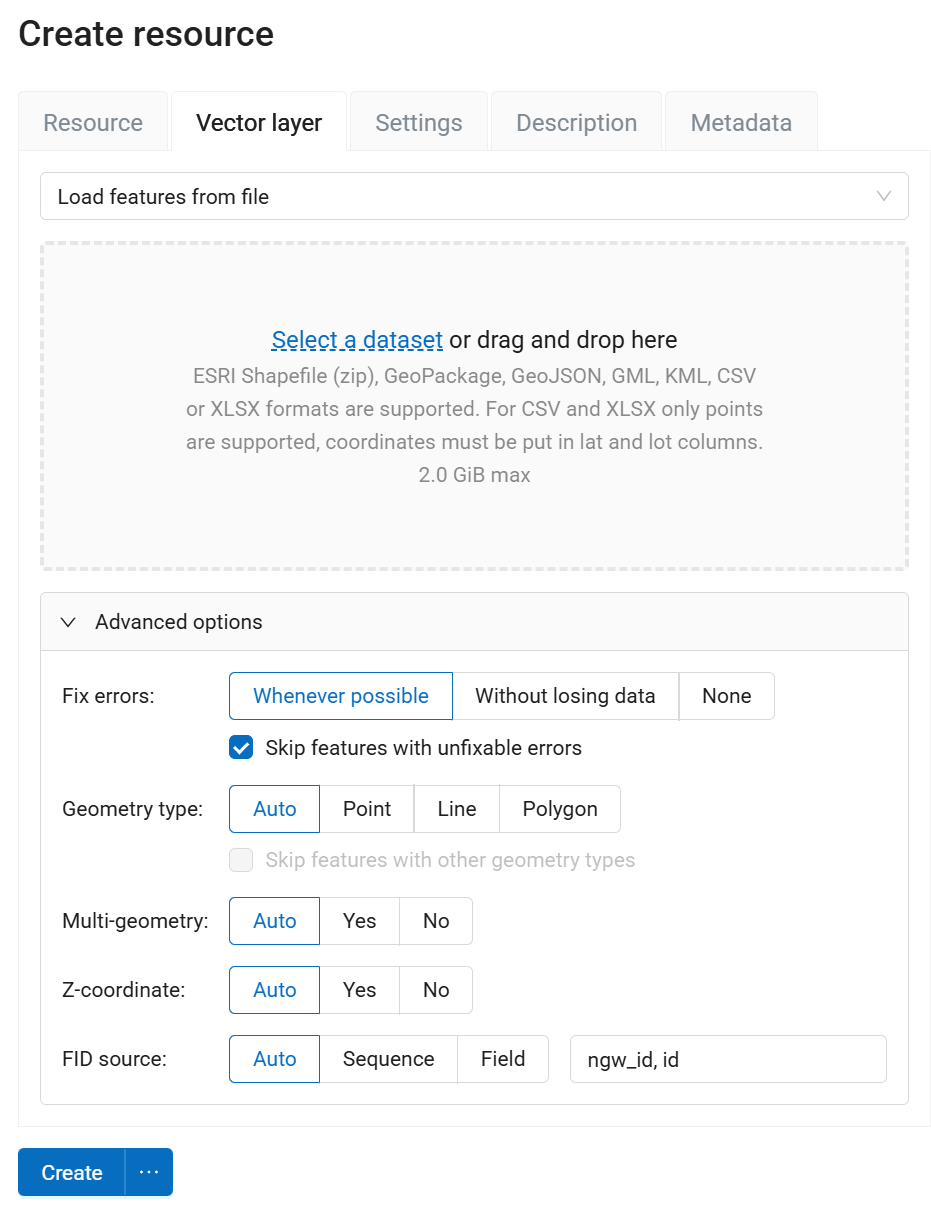
Pic. 7.46. Vector file upload tab
In the “Resource” tab enter the name of the vector layer (Pic. 7.47.). It will be displayed in the admin interface. The “Key” field is optional.
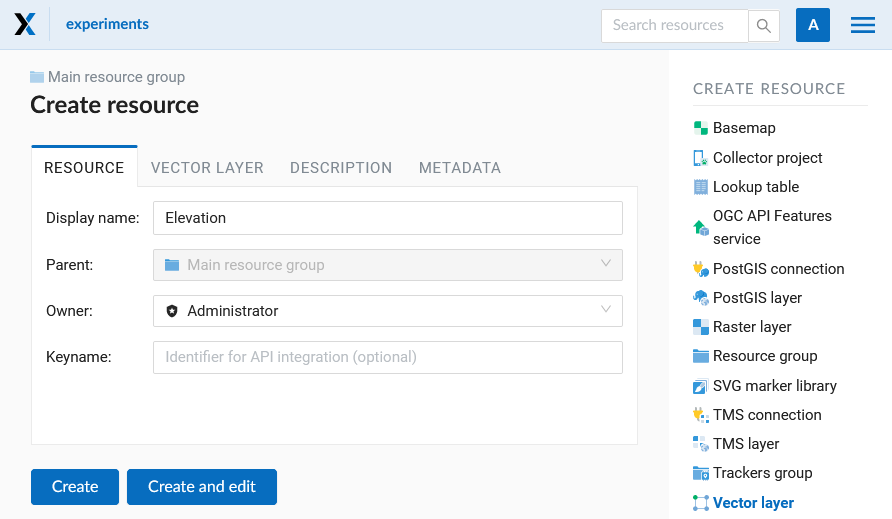
Pic. 7.47. Vector layer name
On the “Settings” tab you can enable feature versioning. It allows the layer to be edited directly in QGIS via NextGIS Connect by multiple users at once.
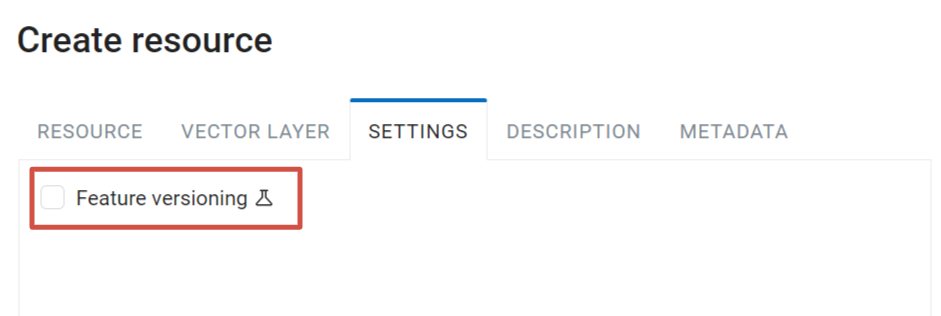
Pic. 7.48. Vector layer settings
If you want all vector layers added to your Web GIS to be versioned by default, it can be set in the Control panel.
Also you can add Description and metadata.
After uploading the file and specifying the parameters, click the Create button.
Then you can create a style that will later visualize the data layer on a Web Map. You can also create a form or data collection.
7.6.1.3. Empty vector layer
Creating an empty vector layer allows you to start a data base in your WebGIS without using a desktop app.
Navigate to the resource group (folder) in which to create a vector layer. Click Create resource button and select Vector layer.

Pic. 7.49. Selecting “Vector layer” resource type
In the opened window use the dropdown menu to select “Create empty layer”. In the field below select geometry type for the layer. By default, a point layer will be created.
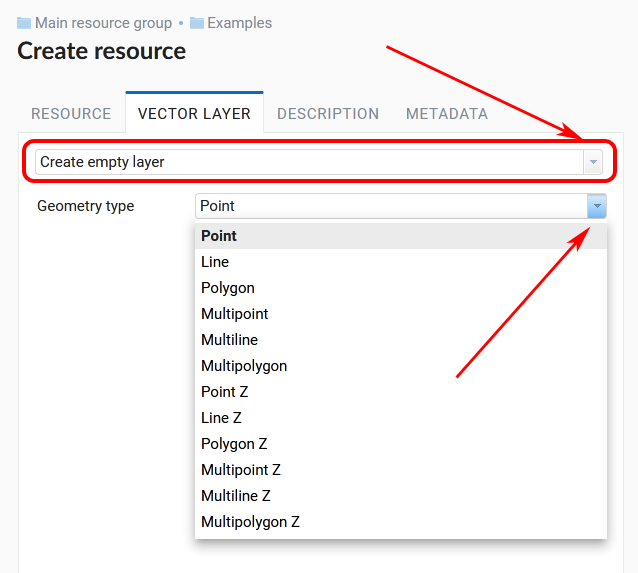
Pic. 7.50. Selecting geometry type for an empty layer
Points, lines and polygons are supported. For any of these geometry types you can select an option with multigeometries and/or Z-coordinate.
On the “Resource” tab enter the name of the vector layer. It will be displayed in the resource list. By default the resource type is used as its display name.
Next, click on the three dots next to the Create button and select Create and edit.
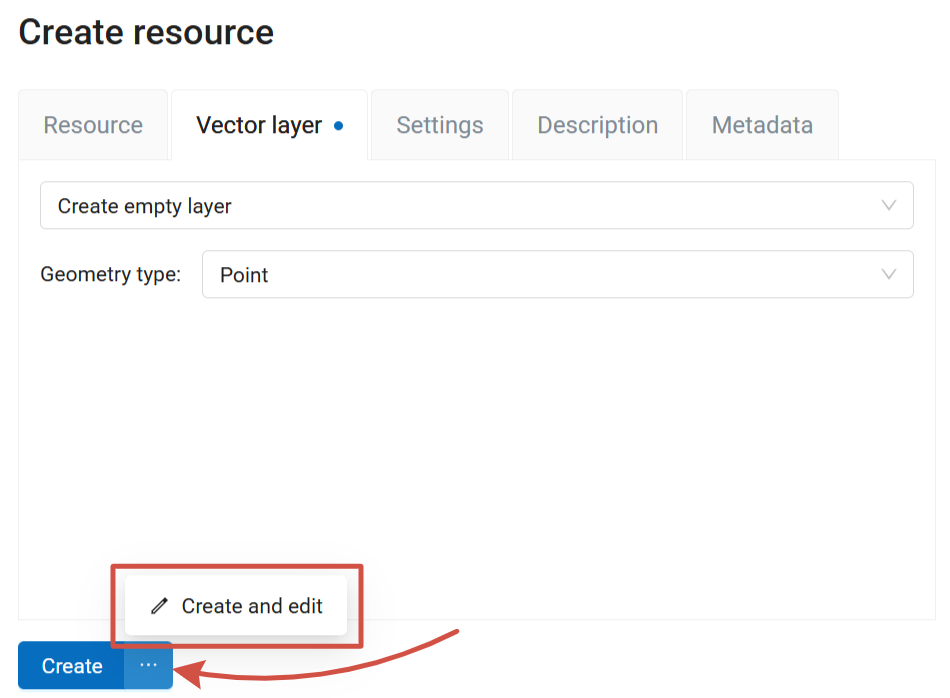
Pic. 7.51. Opening the resource update page immediately after creating the resource
The layer is created and a new tab opens where you can add attributes (fields).
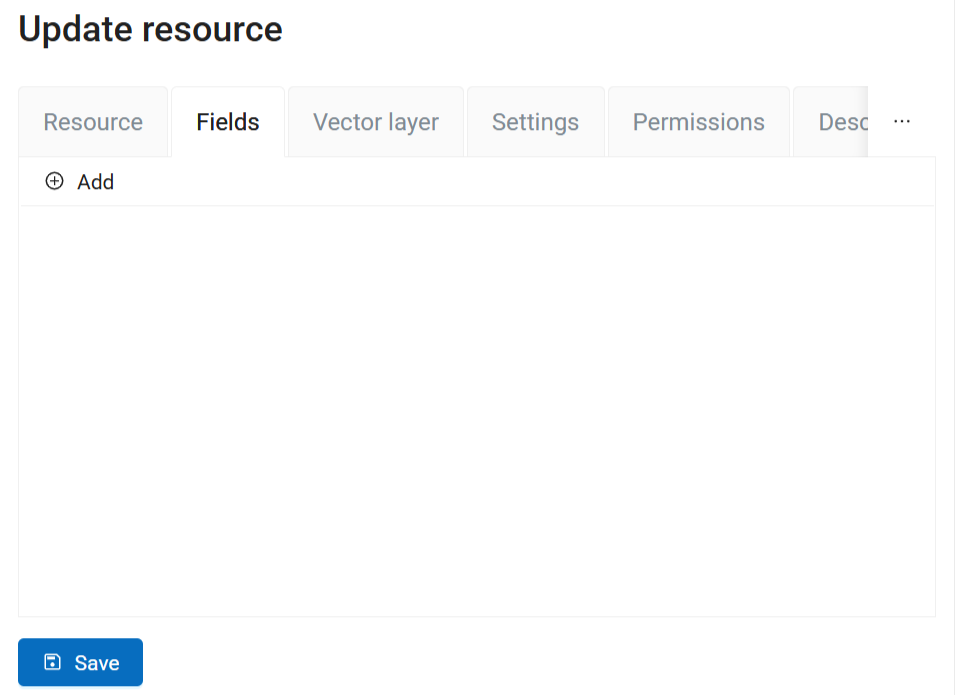
Pic. 7.52. Fields tab
Click  Add. A field is created. Click on it to open the properties dialog.
Add. A field is created. Click on it to open the properties dialog.
Select the data type for the field (numbers: INTEGER, BIGIN, REAL, text: STRING, date and/or time: DATE, TIME, DATETIME).
The name of the field can also be edited.
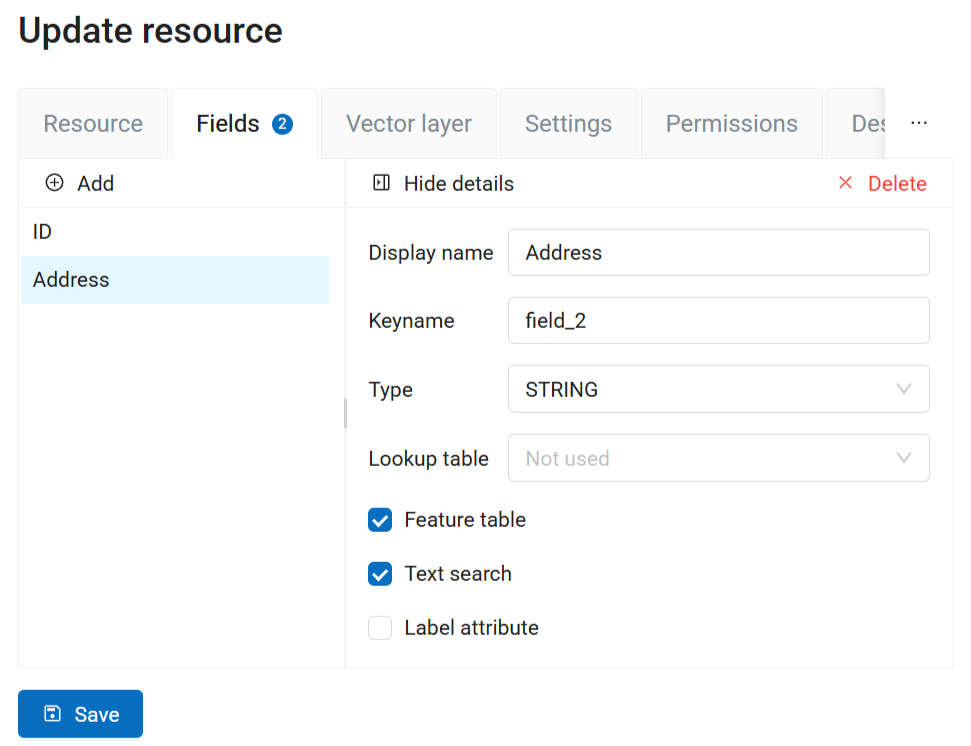
Pic. 7.53. A new field with string data type and “Address” as a custom name
Click  Hide detaild to return to the list of fields.
Hide detaild to return to the list of fields.
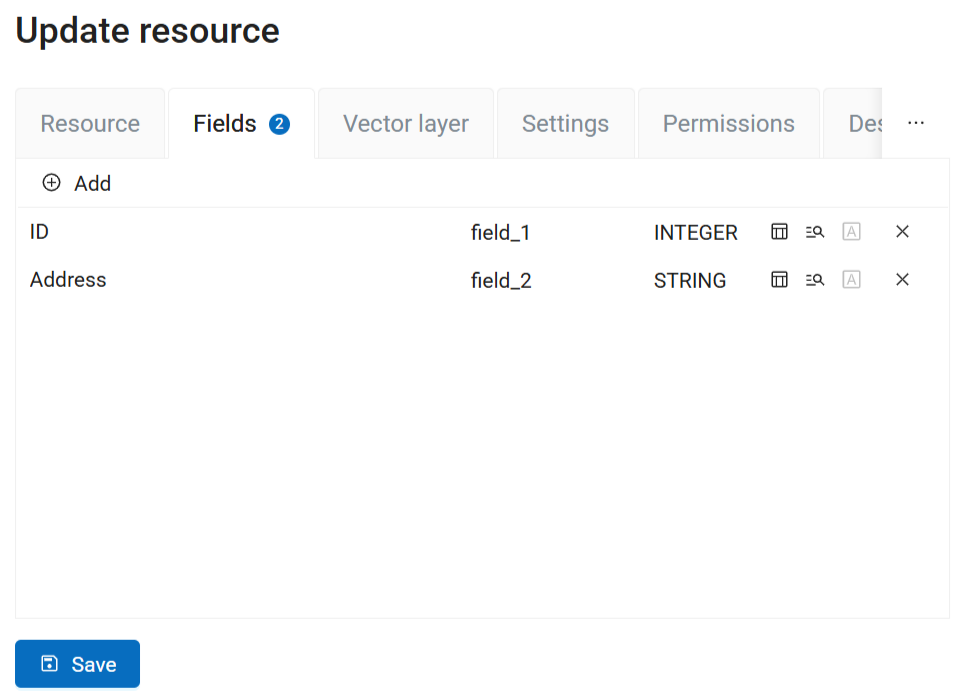
Pic. 7.54. Field list
When all the necessary fields are added, click Save.
Later you can edit the fields.
Now you can create a style that will later visualize the data layer on a Web Map.
To add features to the newly created layer you can use the editing toolbar.
7.6.2. Raster layer
Raster images in NextGIS Web should be loaded using the “Raster Layer” special resource.
7.6.2.1. Requirements for uploaded files
Data must be georeferenced and have valid reference system description in GeoTIFF tags.
Supported format:
GeoTIFF or ZIP-archived GeoTIFF;
georeferenced JPEG or PNG in a ZIP-archive containing the image file and the *.aux.xml file.
7.6.2.2. Creation process
To add a raster layer navigate to a group where you want to create it. Press Create resource button and select Raster layer (see Pic. 7.55.).
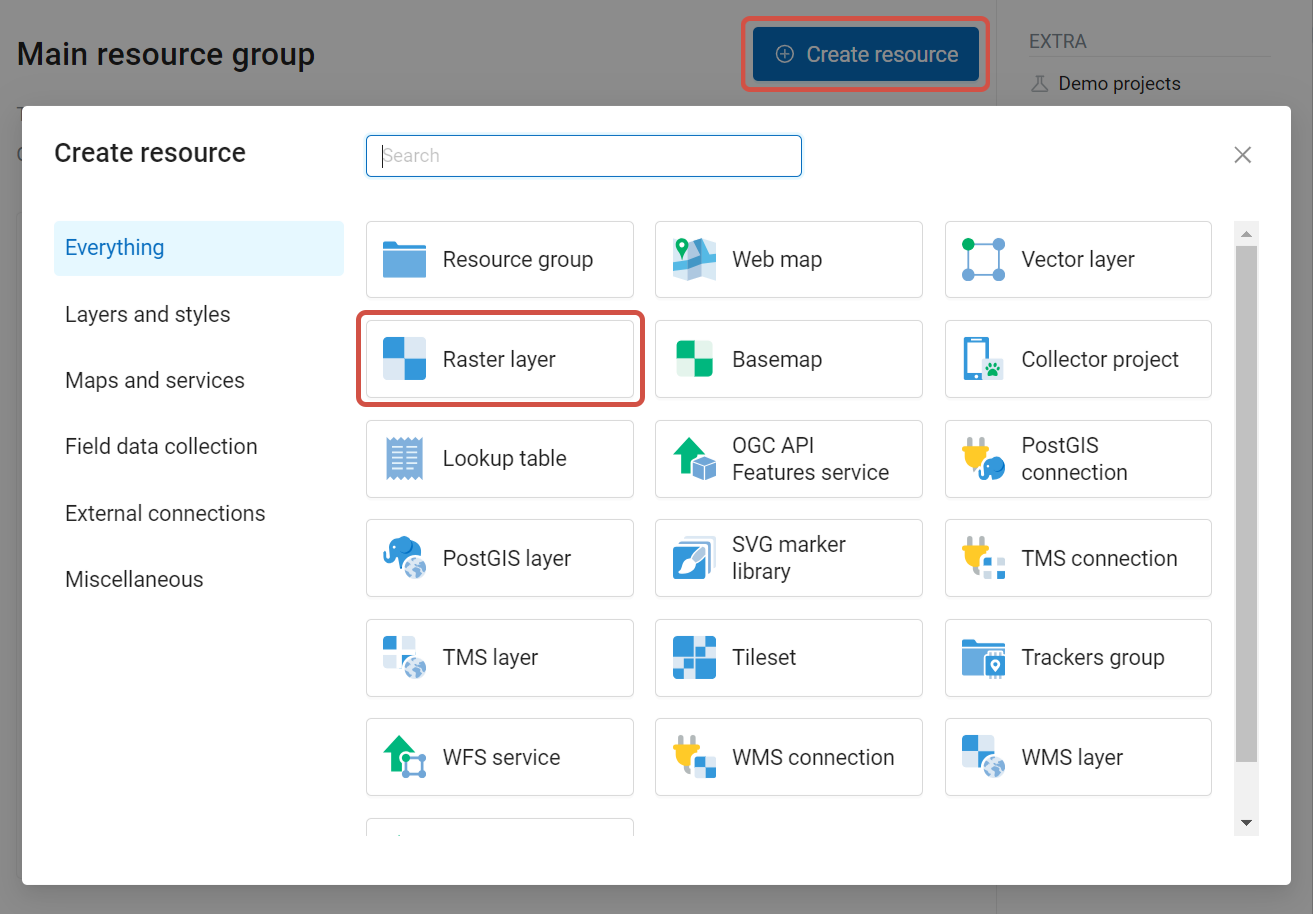
Pic. 7.55. Selection of “Raster layer” resource type
On the “Raster layer” tab you need to upload a geodata file in GeoTIFF format. The upload dialog indicates the maximum file size allowed on your subscription plan (Pic. 7.56.).
If you plan to use this raster in QGIS directly from your Web GIS, tick the Upload as Cloud Optimized GeoTIFF (COG) checkbox. This will optimize the raster to ensure fast display.
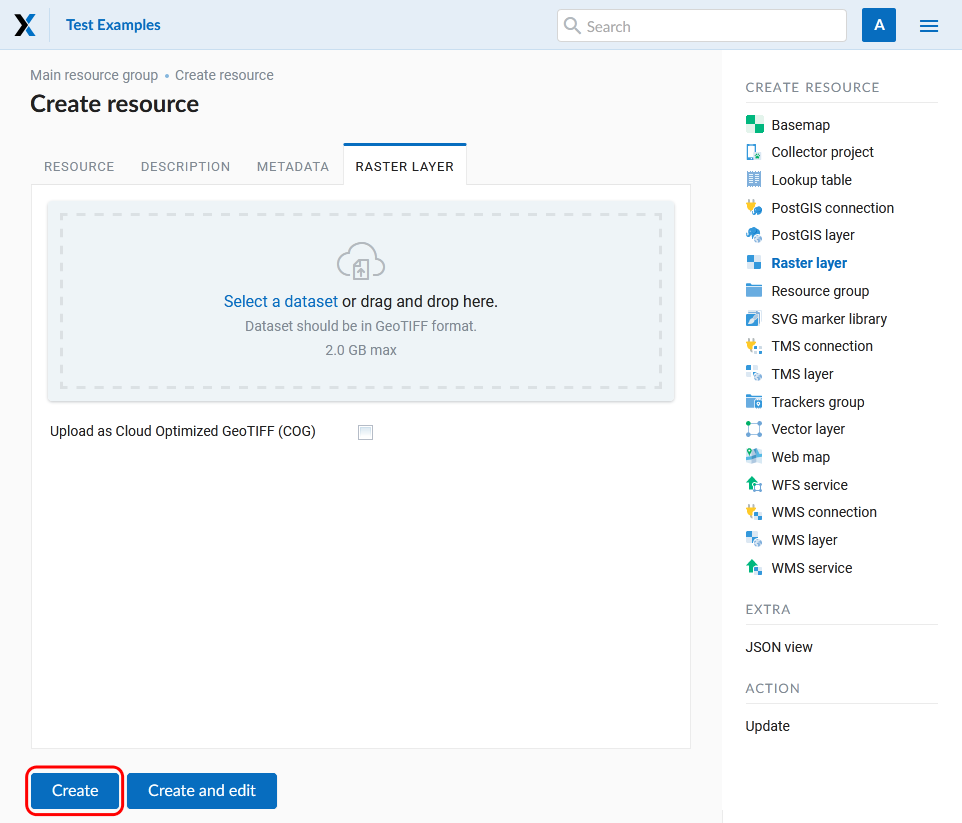
Pic. 7.56. Uploading raster file
In the “Resource” tab specify the name of the raster layer (see Pic. 7.57.). It will be displayed in the admin interface. The “Key” field is optional.
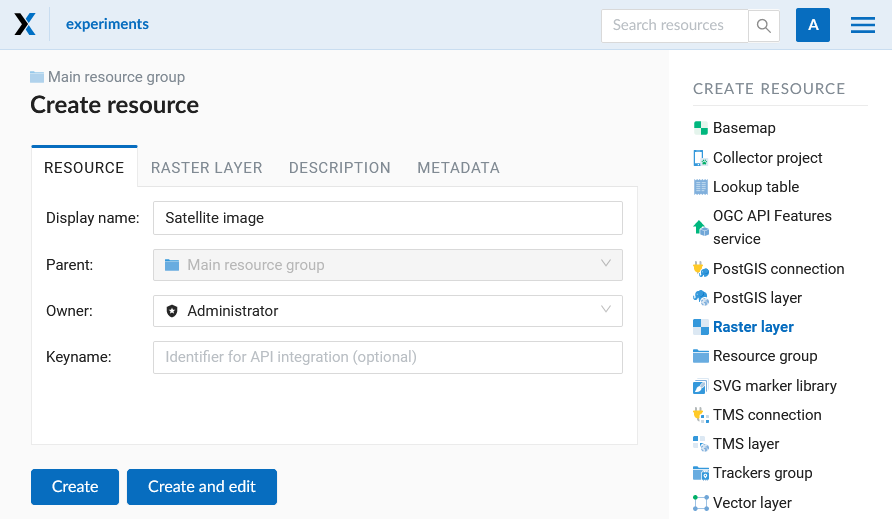
Pic. 7.57. Raster layer name
Also you can add Description and metadata.
To complete click the Create button.
7.6.2.3. Uploading big rasters
Satellite images of high resulution and other rasters may be very large. The file size is not representative because data is compressed. The actual data size may be much bigger. To make sure that raster data is quickly rendered on a Web Map and services work fast raser files must be converted before uploading them o Web GIS.
There are three limitation for uploading big rasters:
Max file size - it depends on your subscription plan, on Premium by default the limit is 2 GiB. Max file size can be modified to a certain point for cloud Web GIS and indefinitely for on-premise;
Max size of extracted raster in the cloud can be up to 4 GiB. GeoTIFF uses a compression algorithm and the file size may be drastically smaller than the size of the unpacked data. To calculate the size of he decompressed raster multiply the three parameters: pixel count * number of bands * bytes per pixel.
Note
If the raster file does not have alpha channel, it will be added during uploading, further expanding the raster size, so for calculating the data size add +1 channel to the equasion.
Overall data storage of the Web GIS - on Premium you can upload up to 50 GiB of data (this limit can be expanded);
There is no time limit for uploading raster files.
7.6.2.4. Raster layer with transparency (clip or alpha channel)
Most of utilities do not create an alpha channel and only add a NoData value. To transform NoData value to an alpha channel use the command line utility gdalwarp. Here is an example of this command.
gdalwarp -t_srs EPSG:3857 -multi -dstalpha -dstnodata none -wo \
"UNIFIED_SRC_NODATA=YES" -co COMPRESS=JPEG \
d:\temp\o\ast_20010730_010043_rgb.tif d:\temp\o\ast_20010730_010043_rgba.tif
7.6.2.5. Uploading indexed color rasters
Indexed Color raster files are uploaded just like the RGB raster files. If the file is not in GeoTIFF format, you can convert it as follows:
gdal_translate madison.map madison.tif
7.6.3. Tileset
To add a Tileset, select a Tileset in the “Create Resource” block of operations.
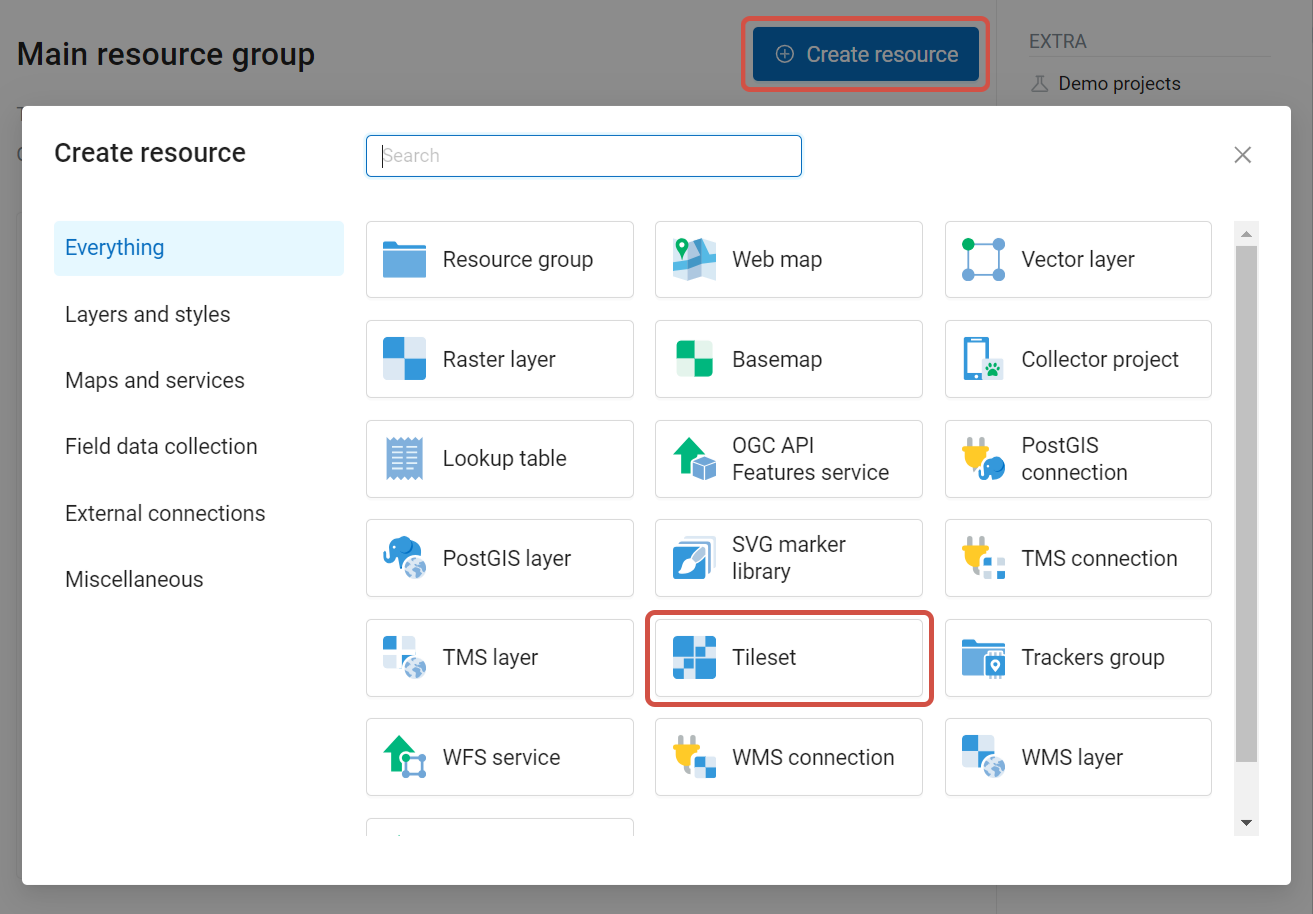
Pic. 7.58. Selecting Tileset resource type
Next, you need to enter the name of the tileset, which will be displayed in the administrative web interface.
The “Key” field is optional. On the appropriate tabs, you can add a resource description and metadata. Typically, metadata is used to develop third-party applications using APIs.
In the “Tileset” tab, you need to upload a tileset in MBTiles format or a zip archive. Tiles must be in PNG or JPEG format and have a size of 256x256 pixels.
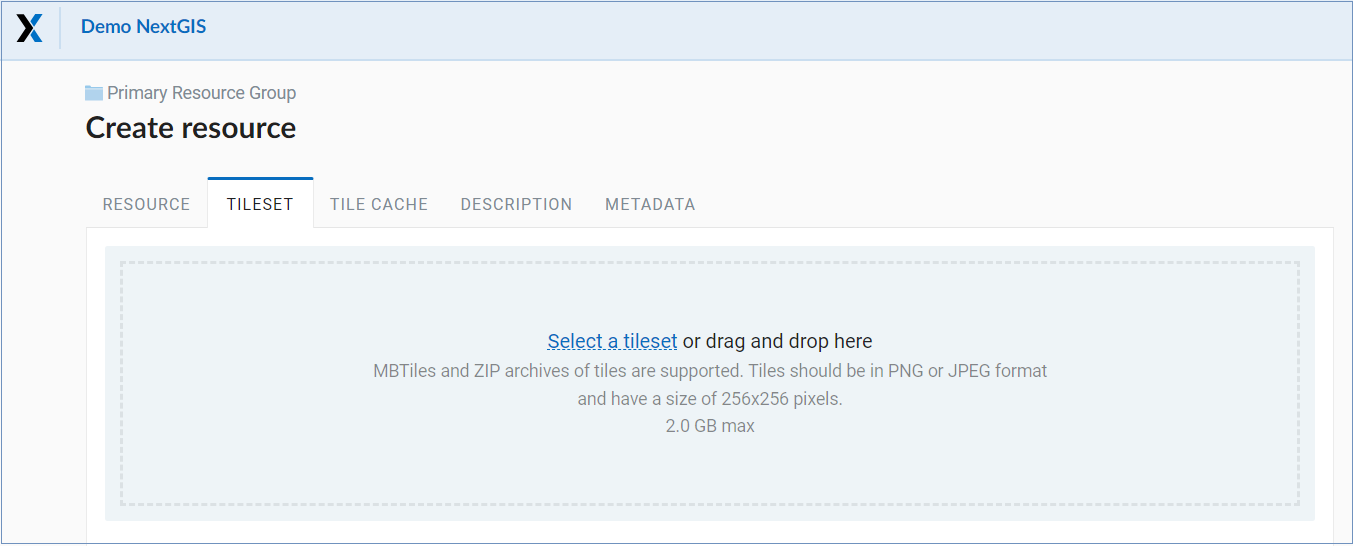
Pic. 7.59. Tileset tab
In the “Tile Cache” tab, the user can set the caching settings:
Enable - enable/disable tile caching;
Allow using tiles in non-tile requests - when requesting an image (not a tile), use cached tiles if available;
Max zoom level - the threshold value above which the cache is not accessed, the map image is rendered on the fly;
TTL, sec (Time to live) - “time to live” or storage of tiles on the server in seconds, after which the image will be re-formed at the next request. If TTL = 0, then the storage time of tiles is not limited;
Flush - write only - clears the tile cache when saving the style.
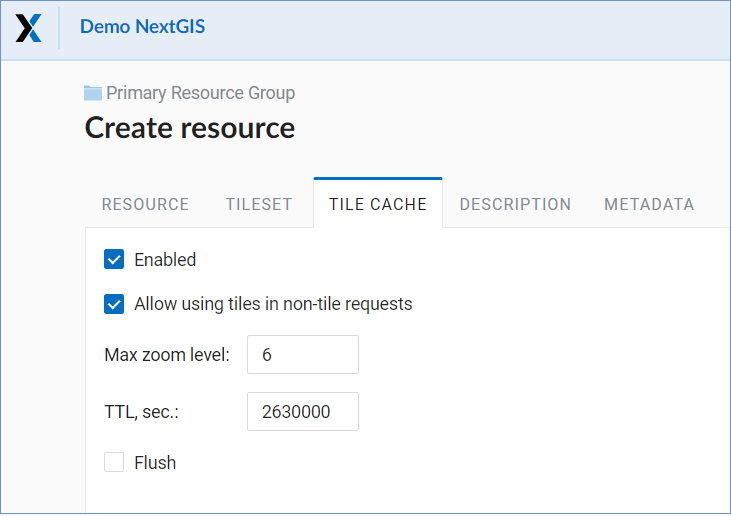
Pic. 7.60. Tileset settings
After filling in all the fields, clicking the Create button completes the process of creating the resource Tileset.
See how to add a tileset in our video:
Watch on youtube.